FREE SHIPPING FOR ORDERS OVER R500 WITHIN SOUTH AFRICA
Free shipping for orders over R500
FREE SHIPPING FOR ORDERS OVER R500 WITHIN SOUTH AFRICA
Free shipping for orders over R500
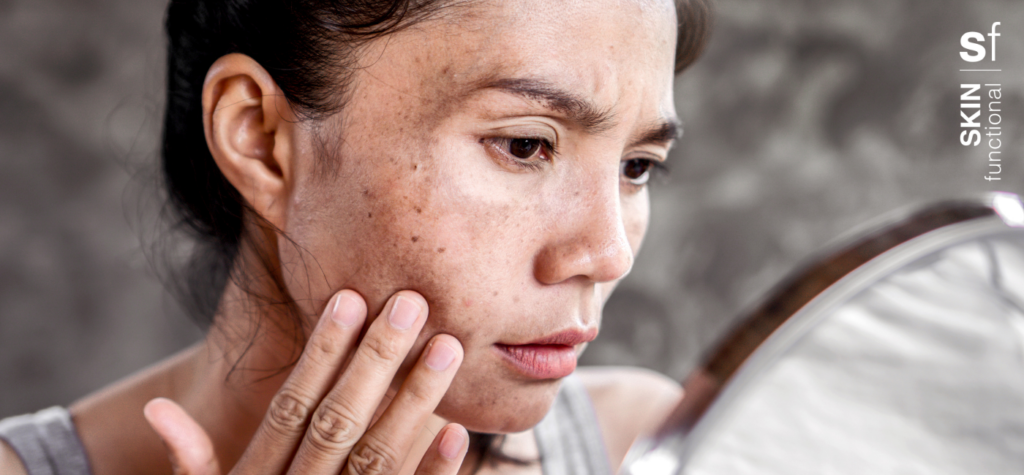

Pigmentation is normal, as it’s what gives your skin its colour. Hyperpigmentation is an overproduction of pigmentation. It appears as tan or dark brown spots and or mottled patches, usually on the forehead, cheeks, upper lip, nose, chin, hands and chest. It is important to remember that hyperpigmentation is a long term management skin concern.
In this article we take a look at the different types of hyperpigmentation, their causes and what you can do to manage it.
What causes skin pigmentation?
When there’s inflammation, your skin cells produce extra pigment during the healing process. This inflammation is caused by the usual suspects – too much sun exposure, ageing, and hormones.
Genetics are also a major factor in melasma, so if you’ve noticed that hyperpigmentation runs in your family, be sure to take special care of your skin and use suitable skincare products to prevent skin hyperpigmentation from worsening.
Types of hyperpigmentation
Age/sun spots
As skin ages, the number of melanin-producing cells decreases, but the remaining ones increase in size and their distribution becomes more focused. After years of exposure to UV light and pollution, melanin builds up and creates small, flat, darkened patches of skin, which are also called age spots, liver spots, sun spots, or solar lentigines. They’re found in the areas frequently exposed to the sun such as the face, neck, chest, hands and arm.
Melasma
Also known as chloasma, melasma is one the most common types of facial hyperpigmentation and the most difficult to manage, and usually occurs between the ages of 20 and 40. It looks similar to age spots, but covers a larger area on the skin, typically on the face. It’s particularly common amongst women, and is thought to be triggered by hormonal changes and medications, sun exposure, and genetic predisposition. Many pregnant women get melasma, which is why it is also known as “the mask of pregnancy”.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
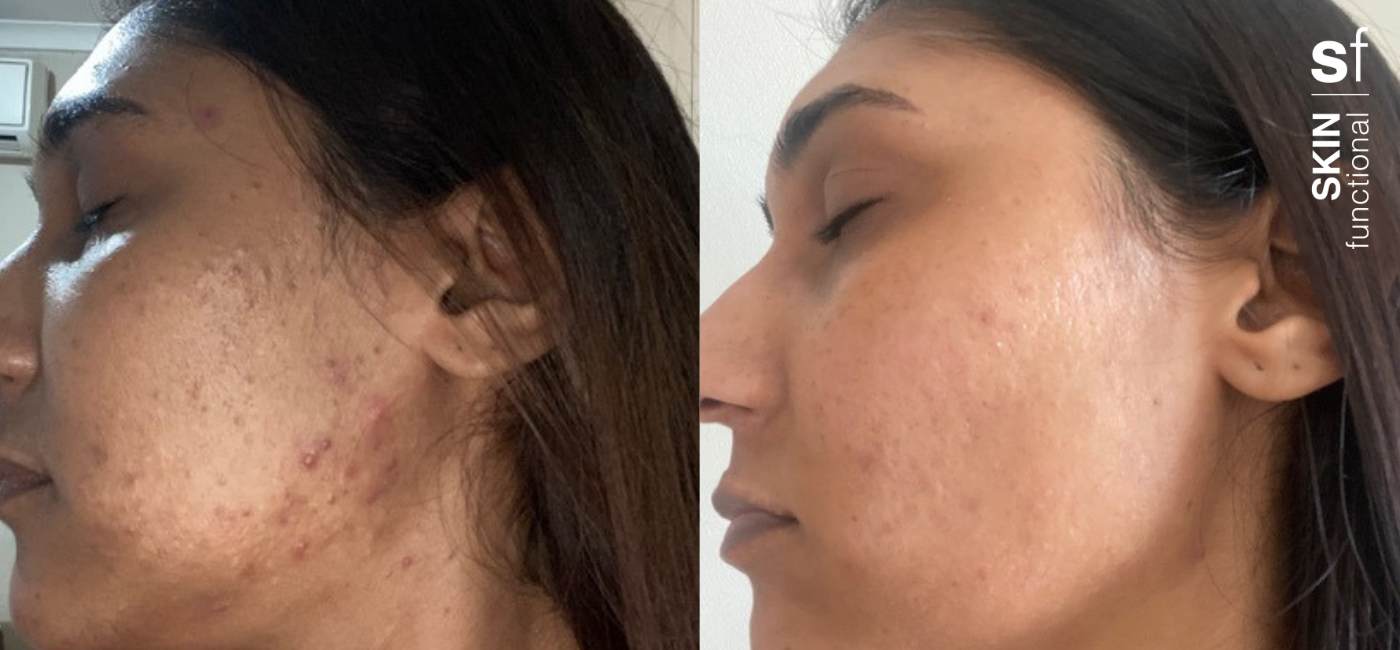
This is a temporary skin condition that occurs when a skin injury or trauma heals and leaves a darkened and discoloured area behind. It’s commonly caused by acne or eczema flare ups, as well as cuts, burns and cosmetic procedures such as dermabrasion, laser treatment and chemical peels.
How to prevent pigmentation
You know how the saying goes: Prevention is better than cure! Here are some steps you can take to prevent hyperpigmentation and dark spots.
Keep an eye on dark spots
Always consult your dermatologist if you’re ever concerned about a dark spot or if it starts to bleed, itch, or change size or colour and this could be a sign of something more sinister.
How to treat existing pigmentation and dark spots?
Now that you’ve armed yourself with knowledge on what dark spots are and their causes, learn about the most effective skincare products to treat hyperpigmentation.
We will give you the right amount of love!
From expert advice, specials and new products, be the first to know.
No spamming, we promise!






Click on the button below and choose 2 free gifts.
Hurry, while stocks last!